Tourette’s disorder is a childhood-onset neuropsychiatric disorder.

It includes both motor and vocal tics, coprolalia (involuntary utterance of obscenities words), and echolalia (repetition of interviewer speech) throughout a period of more than 1 year. The onset is before age 18 years.
Georges Gilles de la Tourette first described the patient with Tourette’s syndrome in 1885.
About 90 percent of persons with Tourette’s disorder have compulsive symptoms, and as many as two-thirds meet the diagnostic criteria for OCD.
Prevalence in childhood 5 to 30 in 10000 population and in adulthood 1 to 2 in 10000 population. M:F = 3:1.
The tics take the form of grimacing forehead puckering, eyebrow-raising; eyelid-blinking, winking, nose-wrinkling, nostril-trembling, mouth-twitching, displaying the teeth, biting the lips and other parts, tongue-extruding protracting the lower jawnodding, jerking, or shaking the headtwisting the neck looking sideways head-rolling; hand-jerking arm-jerking; plucking fingers writhing fingers fist-clenchingshoulder-shrugging foot, knee, or toe shaking walking peculiarlybody writhing jumpinghiccupping; sighing yawning snuffingblowing through the nostrils whistlingbelchingsucking or smacking sounds and clearing the throat.
Etiology: Genetic, neurochemical (dopamine), or immunological (autoimmunity) multifactorial causes are found behind this Tourette’s syndrome.
Treatment:
Typical anti-psychotic (Haloperidol, Pimozide) or atypical antipsychotic (Risperidone, Olanzapine), CLonidine (alpha-1 adrenergic agonist) and psychotherapy (Habit reversal technique) is effective.
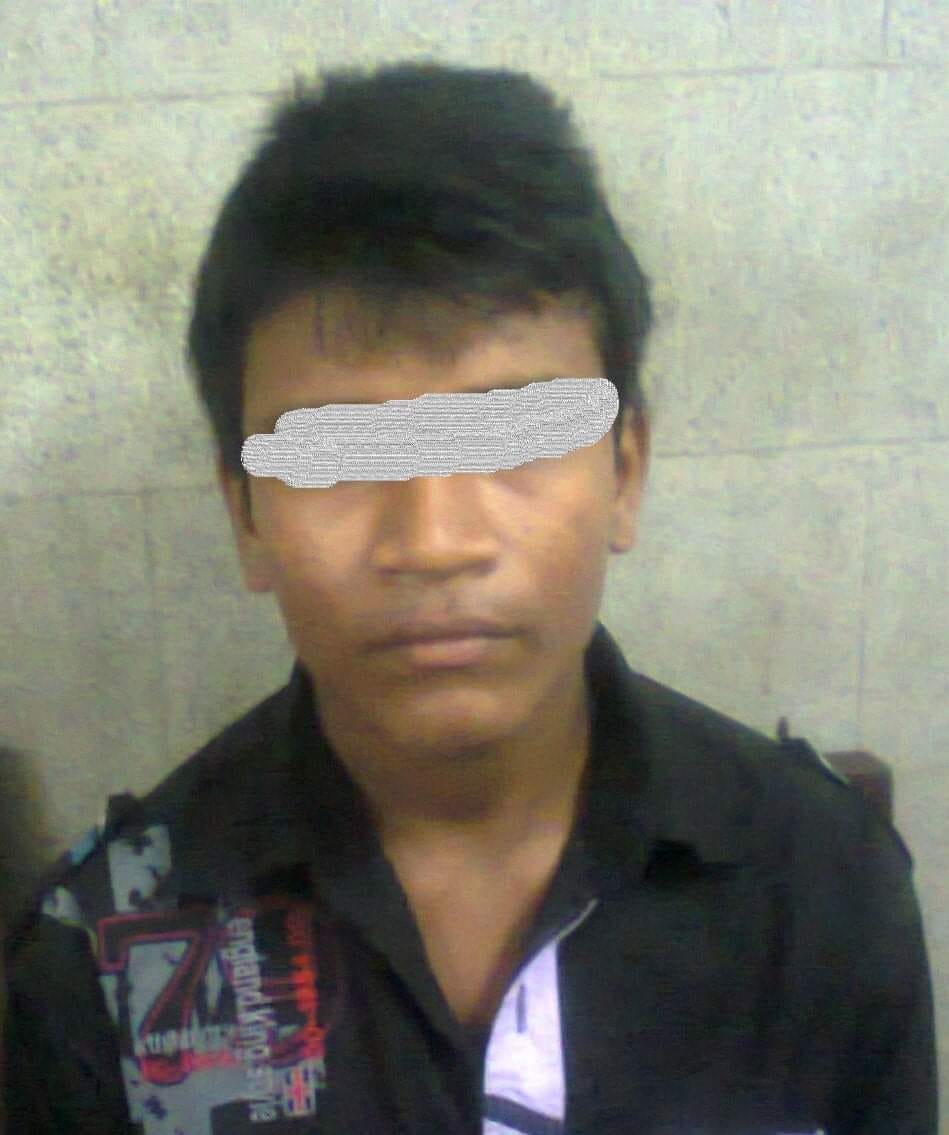
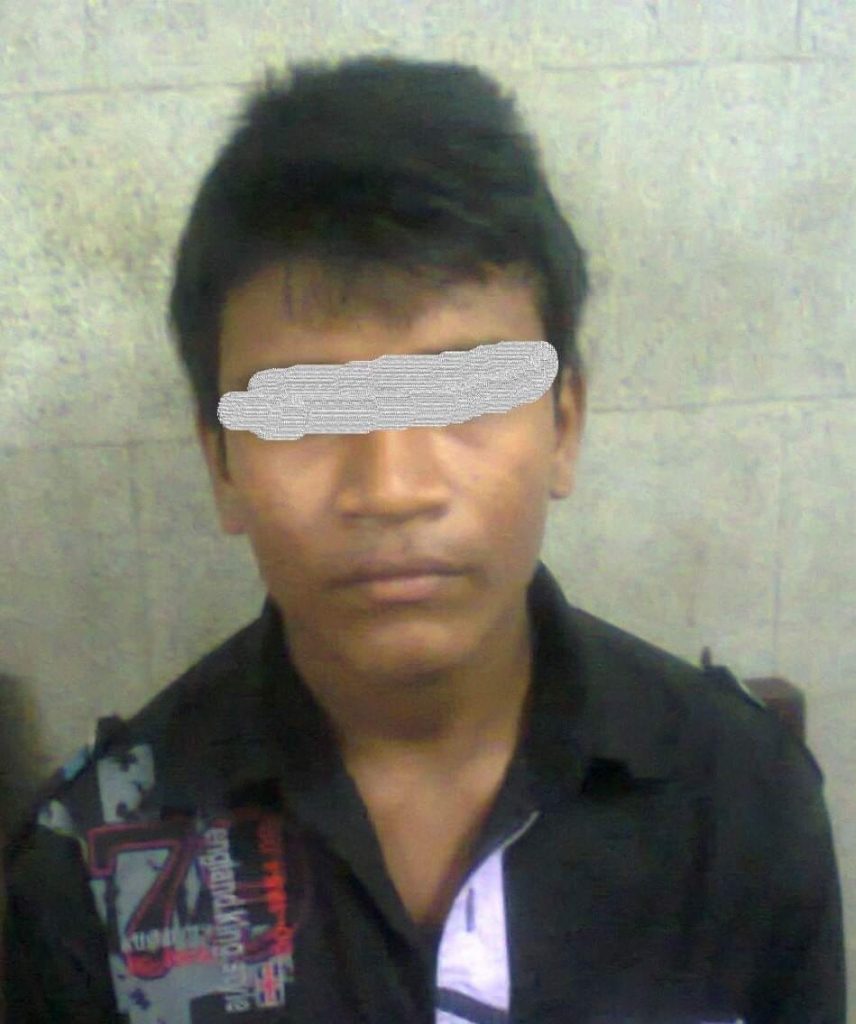
The picture of the boy (below) who was suffering from Tourette’s syndrome now completely recover.